AML CTF Algeria: Compliance Insights & Crypto Risks
When you start dealing with digital assets in Algeria, the first thing to get straight is AML CTF Algeria, the joint anti‑money laundering (AML) and counter‑terrorist financing (CTF) regime that governs crypto activities in the country, also known as Algerian AML/CTF compliance. This framework AML CTF Algeria is more than a legal footnote; it dictates who can launch a token, how exchanges must verify users, and what reporting triggers a regulator’s alarm. It encompasses national compliance requirements, requires robust transaction monitoring, and influences the design of any blockchain‑based service operating locally. Below we’ll walk through the core pieces you need to know and why they matter for every crypto project, trader, or investor in the region.
Core Elements and Their Relationships
First, Anti‑Money Laundering (AML), the set of policies that prevent illicit funds from entering the financial system obliges every platform to collect full KYC details, keep detailed logs, and flag suspicious patterns. Counter‑Terrorist Financing (CTF), rules aimed at stopping money from reaching extremist groups adds a layer of screening against sanctioned entities and high‑risk jurisdictions. Together, they form the backbone of Algeria’s crypto oversight. Algerian Financial Regulations, the national laws that codify AML/CTF duties for banks, fintechs, and crypto exchanges tie these concepts to concrete penalties, ranging from fines to license revocation. Finally, the global FATF Guidelines, the international standards that shape AML and CTF policies worldwide act as the upstream driver, pushing Algeria to adopt stricter reporting thresholds and enhanced due‑diligence checks. In practice, a local exchange must (1) run identity verification on every user, (2) monitor transaction flow for patterns that match money‑laundering typologies, (3) submit SAR (Suspicious Activity Report) filings when thresholds are crossed, and (4) regularly audit its compliance program against the latest FATF recommendations. Failure to meet any of these steps can trigger a regulator’s enforcement action, which often includes freezing assets and imposing hefty fines. For token issuers, the same rules apply: you need a verifiable whitelist of participants, clear source‑of‑funds documentation, and a transparent token distribution model that can survive a compliance audit. Understanding these interlocking pieces helps you predict where the regulatory heat will be. If you’re looking at launching a DeFi product, expect stricter KYC on liquidity providers. If you’re a trader, keep an eye on how Algerian banks are tightening cross‑border payment monitoring, because that directly impacts your ability to fund exchanges. The overall picture is a tightly woven network where AML, CTF, national law, and FATF standards all shape the crypto operating environment in Algeria.
Below you’ll find a curated list of articles that dive deeper into related topics: reviews of crypto exchanges that struggle with compliance, guides on airdrop eligibility that highlight AML red flags, analyses of regional regulatory shifts, and practical tips for navigating token launches under Algerian law. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, this collection gives you actionable insight to stay ahead of the compliance curve and protect your portfolio from hidden risks.
Algeria's Crypto Ban: How Law No. 25‑10 Is Enforced
By Robert Stukes On 19 Oct, 2025 Comments (23)
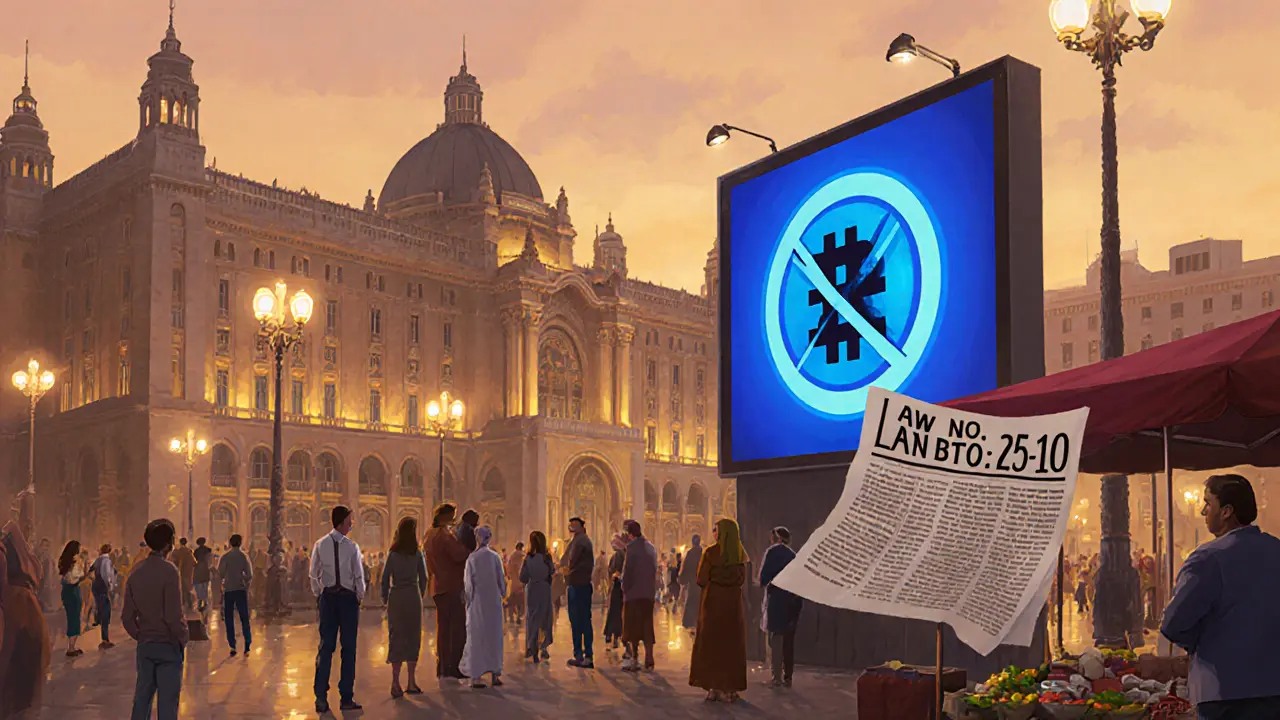

Algeria's Law No. 25‑10 bans all crypto activities, imposes prison and fines, and is enforced by multiple agencies. This article explains the law, enforcement, global context, and practical impacts for users and businesses.
View More